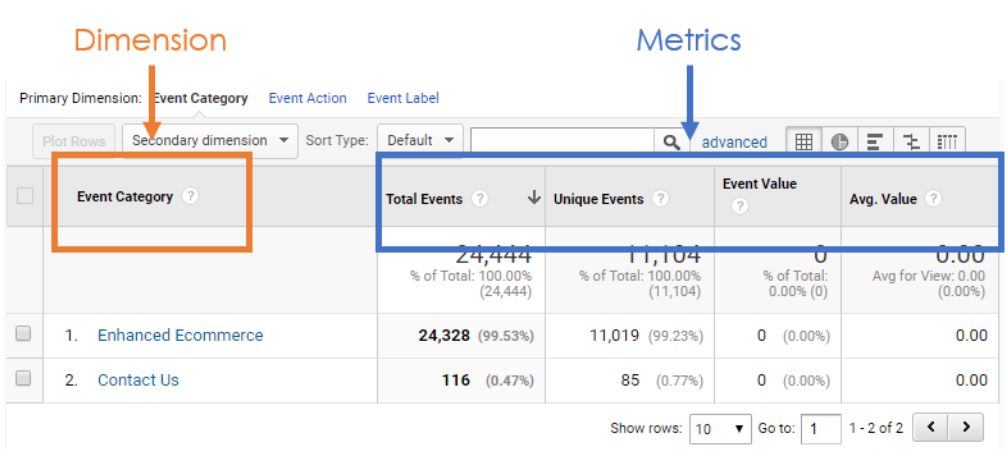
Opening the Power of Second Dimension Analytics for Improved Data Insights and Decision-Making
In the realm of data analytics, main measurements commonly take the limelight, however the real deepness of understandings lies within the realm of additional dimensions. By taking advantage of the power of additional dimension analytics, organizations can reveal covert fads, discover relationships, and extract much more purposeful final thoughts from their information.
Value of Secondary Dimensions
Discovering the importance of second measurements in analytics introduces the covert layers of information insights essential for notified decision-making in numerous domain names. Secondary dimensions give a deeper understanding of main information by supplying extra context and point of views. By integrating additional measurements into analytics, companies can remove a lot more nuanced and extensive understandings from their datasets.
One key significance of second measurements is their capacity to section and categorize main data, permitting an extra comprehensive analysis of specific subsets within a dataset. When looking at the data as a whole, this segmentation enables businesses to recognize patterns, fads, and outliers that could not be evident. In addition, second dimensions aid in uncovering correlations and dependencies between different variables, causing more accurate projecting and anticipating modeling.
Moreover, second measurements play an important role in improving information visualization and coverage. By including secondary measurements to visualizations, such as charts or charts, experts can create extra interesting and insightful depictions of information, promoting far better interaction of searchings for to stakeholders. In general, the assimilation of additional measurements in analytics is instrumental in unlocking the complete capacity of data and driving evidence-based decision-making.
Trick Benefits of Utilizing Secondary Measurements
Using additional measurements in analytics uses organizations a calculated advantage by increasing the depth and granularity of data understandings. One key benefit of incorporating secondary measurements is the capability to section and filter data, allowing for a much more detailed analysis of particular aspects within a dataset. This division makes it possible for companies to gain an extra nuanced understanding of their target market, efficiency metrics, and various other vital data points. By dissecting data using second measurements such as time, location, tool kind, or customer demographics, companies can uncover patterns, fads, and relationships that may or else remain concealed.
Furthermore, the usage of secondary measurements boosts the context in which primary information is interpreted. By leveraging additional measurements in analytics, organizations can harness the full potential of their information to drive far better decision-making and achieve their organization purposes.
Advanced Data Evaluation Techniques
A deep study advanced data analysis techniques exposes advanced methods for drawing out important understandings from complicated datasets. One such method is device learning, where algorithms are employed to determine patterns within information, anticipate end results, and make data-driven decisions. This approach permits for the automation of logical version building, making it possible for the processing of big volumes visit this site of information at a much faster rate than standard methods.
One more sophisticated technique is predictive analytics, which makes use of statistical algorithms and equipment knowing techniques to forecast future outcomes based on historic data. By analyzing patterns and trends, businesses can prepare for consumer habits, market patterns, and potential threats, equipping them to make proactive decisions.
Moreover, message mining and view evaluation are valuable methods for drawing out understandings from unstructured information resources such as social media sites comments, client evaluations, and survey reactions. By assessing message data, organizations can recognize consumer viewpoints, identify emerging patterns, and improve their items or solutions based on responses.
Enhancing Decision-Making Via Secondary Dimensions
Enhancing decision-making via secondary dimensions enables companies to make more educated and targeted tactical selections. For instance, by segmenting client information based upon second dimensions like buying history or involvement levels, business can tailor their advertising techniques to specific target market sections, bring about boosted conversion prices and client fulfillment. Furthermore, secondary dimensions can help recognize relationships and relationships in between different variables, allowing companies to make data-driven decisions that drive growth and productivity.
Implementing Additional Measurement Analytics
When incorporating second measurements in analytics, organizations can unlock much deeper understandings that drive tactical decision-making and enhance overall performance. Carrying out second measurement analytics calls for an organized approach to make sure reliable application of this powerful device. The initial step is to determine the essential metrics and dimensions that straighten with the company's strategic objectives. This entails recognizing the certain inquiries the company looks for to respond check out here to and the information points required to address them.
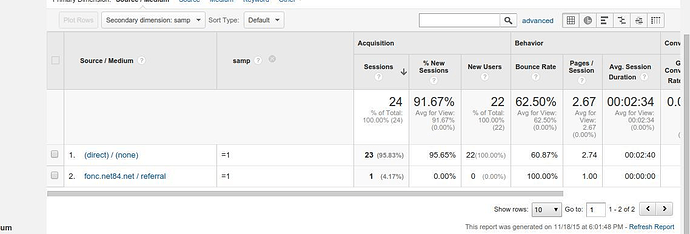
Additionally, companies should take advantage of advanced analytics devices and innovations to simplify the procedure of incorporating additional dimensions. These tools can automate information processing, evaluation, and visualization, allowing companies to concentrate on translating understandings rather than hand-operated information manipulation.
Conclusion
In verdict, secondary dimension analytics play a vital function in improving data insights and decision-making procedures. By utilizing advanced information evaluation techniques and executing additional measurements successfully, organizations can open the power of their information to drive critical organization choices.
In the realm of information analytics, primary dimensions commonly take the limelight, however the real depth of understandings exists within the realm of additional measurements.Making use of second measurements in analytics supplies companies a calculated advantage by increasing the deepness and granularity of information understandings. By leveraging second dimensions in analytics, organizations can harness the complete potential of their data to drive much better decision-making and accomplish their organization objectives.
Implementing data validation processes and normal audits can aid keep information quality and dependability.
By utilizing advanced information analysis techniques and executing second dimensions properly, companies can unlock the power of their information to drive calculated service decisions.